Neumol Pediatr 2016; 11 (2): 71 - 75
C o n t e n i d o d i s p o n i b l e e n h t t p : / / www. n e umo l o g i a - p e d i a t r i c a . cl
74
Actualización en el tratamiento del asma crónica en niños
CONCLUSIONES
Los pilares fundamentales del tratamiento del
asma crónica son la educación, el manejo ambiental y la
farmacoterapia. Los corticoides inhalados son los fármacos de
primera línea para el control del asma. Existen nuevas terapias
promisorias. Se propone un tratamiento escalonado por pasos
y debe evaluarse la técnica inhalatoria, adherencia, exposición
ambiental, presencia de comorbilidades y diagnóstico diferencial
antes de modificar la terapia.
Conflicto de intereses: el autor declara haber sido
invitado como asistente a cursos nacionales por Laboratorio
GlaxoSmithKline.
REFERENCIAS
1.
Papadopoulos NG, Arakawa H, Carlsen KH, Custovic A, Gern
J, Lemanske R et al. International consensus on (ICON)
pediatric asthma. Allergy 2012;67(8):976-97
2.
Mallol J, Aguirre V, Aguilar P, Calvo M, Amarales L, Arellano P
et al. Changes in the prevalence of asthma in Chilean school
age children between 1994 and 2002. International Study
of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC)-Chile phases I
and III. Rev Med Chi. 2007;135(5):580-6
3.
Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention
GINA. Update 2015.
http://www.ginasthma.org4.
Guevara JP, Wolf FM, Grum CM, Clark NM. Effects of
educational interventions for self management of asthma
in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-
analysis. BMJ 2003;326(7402):1308-9
5.
Bacharier LB, Boner A, Carlsen KH, Eigenmann PA, Frischer T,
Gotz M et al. Diagnosis and treatment of asthma in childhood:
a PRACTALL consensus report. Allergy 2008;63(1):5-34
6.
Henderson AJ. The effects of tobacco smoke exposure on
respiratory health in school-aged children. Paediatr Respir
Rev 2008;9(1):21-7
7.
Chilmonczyk BA, Salmun LM, Megathlin KN, Neveux LM,
Palomaki GE, Knight GJ et al. Association between exposure
to environmental tobacco smoke and exacerbations of
asthma in children. N Engl J Med 1993;328(23):1665-9
8.
Rodrigo GJ, Castro-Rodriguez JA. Anticholinergics
in the treatment of children and adults with acute
asthma: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Thorax
2005;60(9):740-6
9.
Vezina K, Chauhan BF, Ducharme FM. Inhaled anticholinergics
and short-acting beta(2)-agonists versus short-acting
beta2-agonists alone for children with acute asthma in
hospital. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;7:CD010283
10. Barnes PJ. Inhaled glucocorticoids for asthma. N Engl J Med
1995;332(13):868-75
11. Holmgren L. Corticoides Inhalados. Neumol Pediatr
2006;1(2):73-6
12. Zhang L, Axelsson I, Chung M, Lau J. Dose response of
inhaled corticosteroids in children with persistent asthma: a
systematic review. Pediatr 2011;127(1):129-38
13. Long-term effects of budesonide or nedocromil in children
with asthma. The Childhood Asthma Management Program
Research Group. N Engl J Med 2000;343(15):1054-63
14. Agertoft L, Pedersen S. Effect of long-term treatment with
inhaled budesonide on adult height in children with asthma.
N Engl J Med 2000;343(15):1064-9
15. Lipworth BJ. Leukotriene-receptor antagonists. Lancet
1999;353(9146):57-62
16. Drazen JM, Israel E, O’Byrne PM. Treatment of asthma with
drugs modifying the leukotriene pathway. N Engl J Med
1999;340(3):197-206
17. Price D, Musgrave SD, Shepstone L, Hillyer EV, Sims
EJ, Gilbert RF et al. Leukotriene antagonists as first-
line or add-on asthma-controller therapy. N Engl J Med
2011;364(18):1695-707
18. Garcia Garcia ML, Wahn U, Gilles L, Swern A, Tozzi CA, Polos
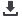
Tabla 3.
Tratamiento escalonado en niños menores de 5 años
Educación
Manejo ambiental
Agonistas beta-2 de acción corta según necesidad
Controlador
de
elección
Otras opciones
de
controladores
Corticoides inhalados
dosis bajas
Antileucotrienos
Corticoides inhalados
uso intermitente
Corticoides inhalados
“doble” dosis bajas
Corticoides inhalados
dosis bajas
+
Antileucotrienos
Referir a especialista
Agregar
Antileucotrienos
PASO 1
PASO 3
PASO 2
PASO 4