255
Criterio de alta
- Clínico: Normalización respiratoria, afebril y mejoría del estado general.
- Radiológico: Imágenes radiológicas en regresión o estabilización de lesiones residuales.
- Tendencia a normalizar los índices hematológicos.
Control posalta
Deberá controlarse con radiografías seriadas cada 30 días hasta la resolución completa. Ra-
diografía tarda hasta 6 semanas en limpiarse y engrosamiento pleural residual hasta 12 semanas
poscirugía.
Bibliografía
1. Ufuk C. Comparison of the methods of fibrinolysis by tube thoracostomy and thoracoscopic decorti-
cations in children with stage II and III empyema: a prospective randomized study. Pediatr Resp 2011;
3(4):e29.
2. Shen-Hao Lai. Value of Lung Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Outcome Prediction of Pediatric
Community-Acquired Pneumonia with Necrotizing Change. PLOS ONE 2015;10(6):e0130082.
3. Mi Suk Choi. Clinical characteristics of lung abscess in children:15 years experience at two university
hospitals. Korean J Pediatr 2015;58(12):478-483.
4. Moreno-Peres D. Neumonía adquirida en la comunidad: tratamineto de casos complicados y situaciones
especiales. Documento de la Sociedad Española de Infectología Pediátrica y Sociedad Española de Neu-
mología Pediátrica. An Pediatr (Barc) 2015;83(3):217.
5. Lai J-Y. Surgical Management of Complicated Necrotizing Pneumonia in Children. Pediatrics and Neona-
tology 2016;6:1-7.
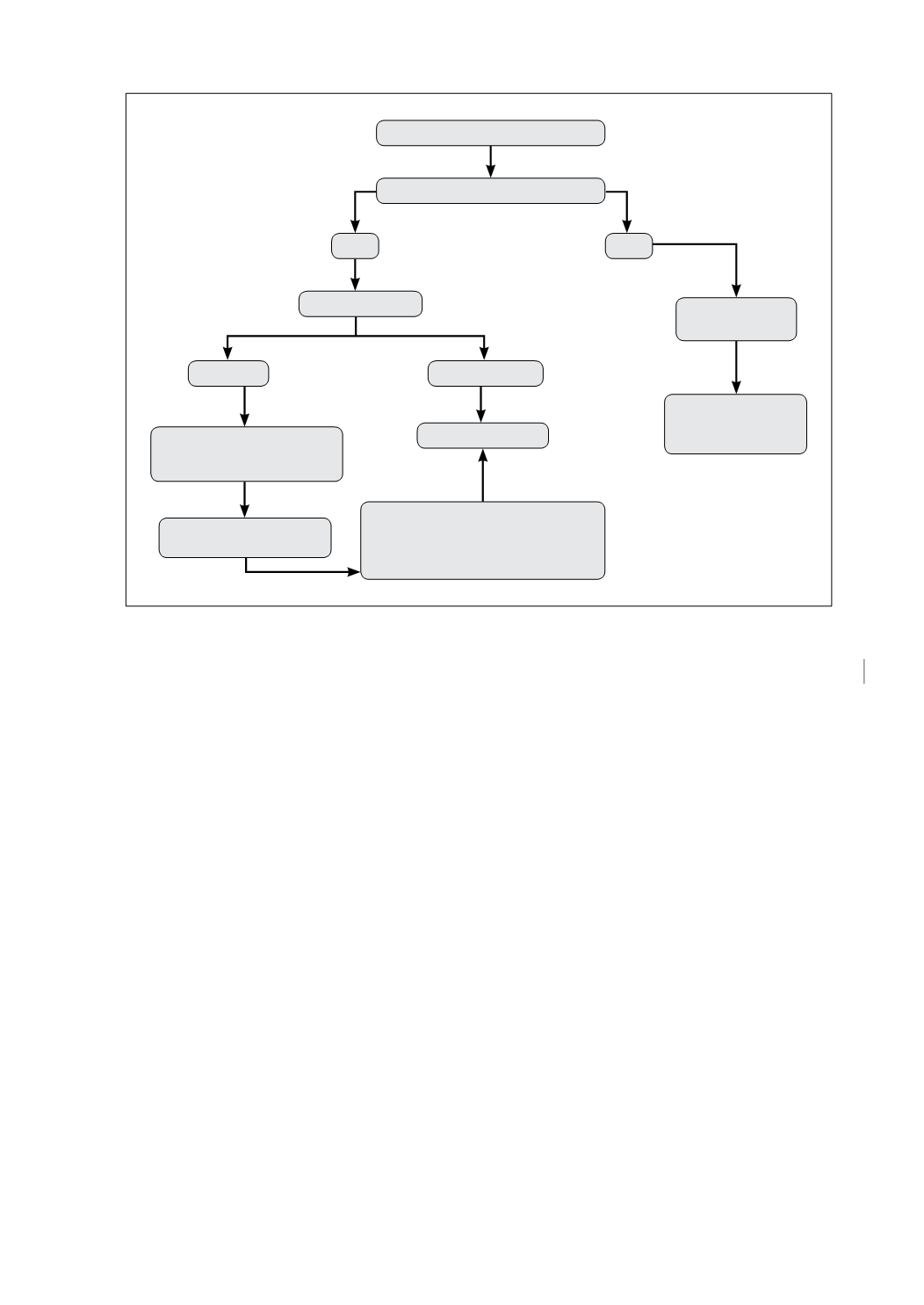
Figura 1.
Rx Tórax por Neumonía
Derrame pleural
Sí
No
Ultrasonido
Libre
Tabicado
Tratamiento
antibiótico
Videocirugía
Mantener antibiótico +
punción y/o drenaje
Control clínico y/o
radiológico
Control clínico y
radiológico
Drenaje parcial + Fiebre,
leucocitosis, PCR1 48-72 horas
Considerar VATS según caso