C o n t e n i d o d i s p o n i b l e e n h t t p : / / www. n e umo l o g i a - p e d i a t r i c a . cl
192
Neumol Pediatr 2017; 12 (4): 187 - 193
Espirometría forzada versus oscilometría de impulso
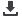
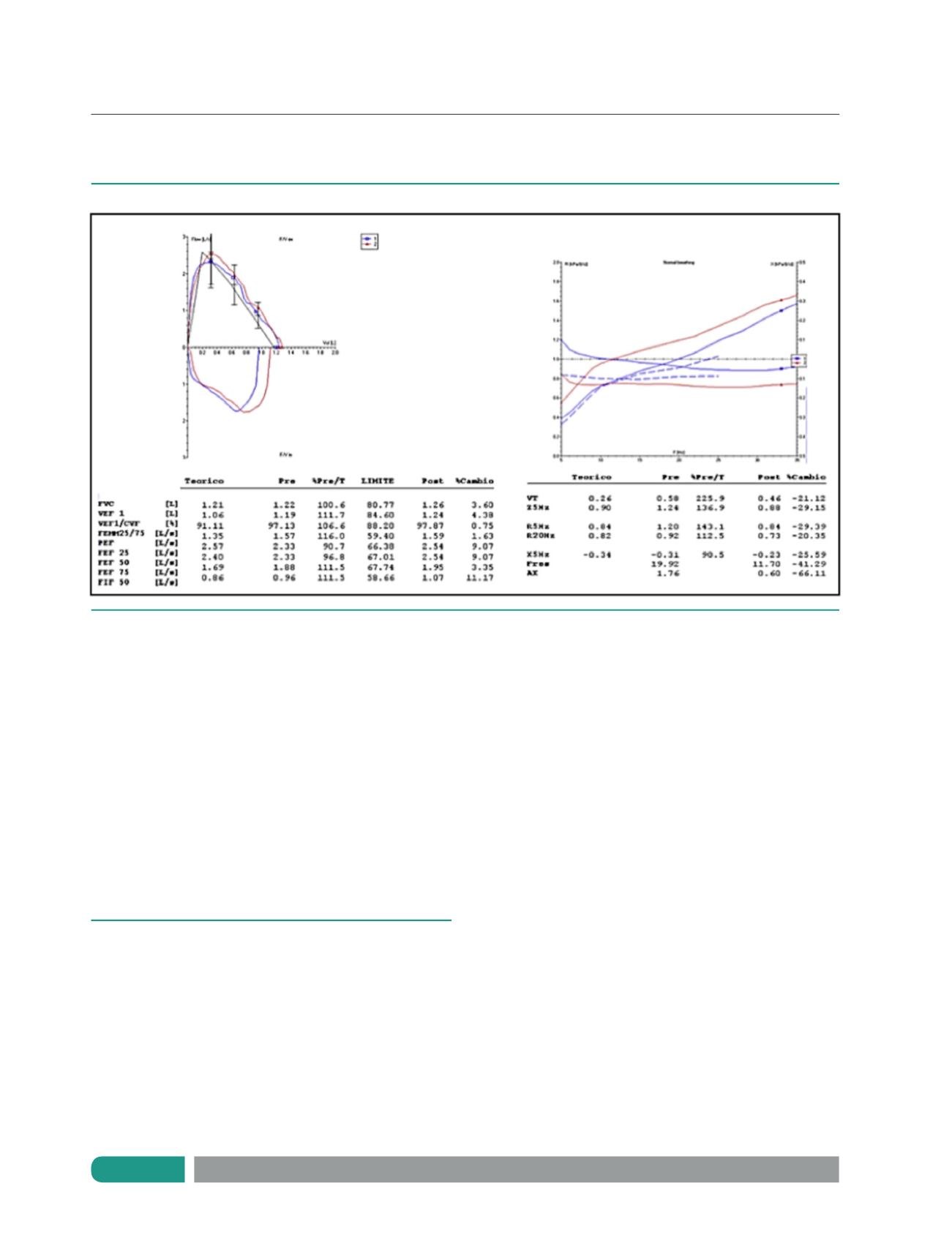
En espirometría no se observan cambios significativos
en volúmenes ni flujos espiratorios forzados luego de la admi-
nistración de 400 ugr de salbutamol. En IOS impedancia (Z5),
resistencia (R5) disminuyen en forma significativa, y reactancia
(x5) aumenta en forma significativa.
El autor declara no presentar conflicto de intereses
Agradecimientos
Deseo agradecer por la revisión de este manuscrito al
Dr. Luis Enrique Vega Briceño con quien comparto mi lugar de
trabajo y al Klgo. Rodrigo Adasme Jeria con quien compartimos
la pasión por la docencia en nuestra profesión.
REFERENCIAS
1.
1. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi
R, Coates A et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir
J 2005;26:319–338.
2.
2. Oostveen E, McLeod D, Lorino H, Farre R, Hantos Z,
Desager K, Marchal F. The forced oscillation technique in
clinical practice: methodology, recommendations and futu-
re developments. Eur Respir J 2003; 22: 1026-41.
3.
3. Arets HG, Brackel HJ, van der Ent CK. Forced expiratory
manoeuvres in children: do they meet ATS and ERS criteria
for spirometry? Eur Respir J 2001;18:655–660.
4.
4.- Eigen H, Bieler H, Grant D, Christoph K, Terrill D, Heil-
man DK, Ambrosius WT, Tepper RS. Spirometric pulmonary
function in healthy preschool children. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med 2001;163:619– 623.
5.
5.- Zapletal A, Chalupova J. Forced expiratory parameters
in healthy preschool children (3–6 years of age). Pediatr
Pulmonol 2003;35: 200–207.
6.
6.- Beydon N, Davis SD, Lombardi E, Allen JL, Arets HG, Au-
rora P et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European
Respiratory Society Statement: Pulmonary Function Testing
in Preschool Children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007;
75: 1323-8.
7.
7.- Cogswell JJ. Forced oscillation technique for determi-
nation of resistance to breathing in children. Arch Dis Child
1973; 48: 259-66.
8.
8.- Vogel J, Smidt U. Impulse Oscillometry - Analysis of
Lung Mechanics in General Practice and the Clinic, Epi-
demiological and Experimental Research. Frankfurt, Pmi
Verlagsgruppe GmbH 1994.
9.
9.- Smith HJ, Reinhold P, Goldman MD. Forced oscillation
technique and impulse oscillometry. Eur Respir Mon 2005;
31: 72-105.
10. 10.- Vink GR1, Arets HG, van der Laag J, van der Ent CK.
Impulse oscillometry: a measure for airway obstruction. Pe-
diatr Pulmonol 2003; 35: 214-219.
11. 11.- Goldman M. Clinical application of forced oscillation.
Pulm Pharm & Therap 2001; 14: 341-50.
12. 12.- Malmberg L, Mieskonen S, Pelkonen A, Kari A, Sovi-
jarvi A, Turpeinen M. Lung function measured by the osci-
llometric method in prematurely born children with chronic
lung disease. Eur Respir J 2000; 16: 598-603.
Figura 3.
Espirometría e IOS de paciente de 7 años: respuesta a broncodilatador solo objetivada con IOS.